Uninterruptible power supply (UPS) batteries store energy and provide backup power when the main power source fails. The technology used in UPS batteries has evolved over time and today a variety of options exist depending on budget, environment, desired lifecycle and even safety requirements.
This article explores the pros and cons behind five major battery types: lead acid, lithium iron phosphate, sodium-ion, lithium-ion and nickel-cadmium. All are leveraged by modern UPS systems; however, newer technology (namely lithium iron phosphate and sodium-ion) are rapidly gaining popularity for their cost-to-performance balance, safety ratings and low environmental impact.
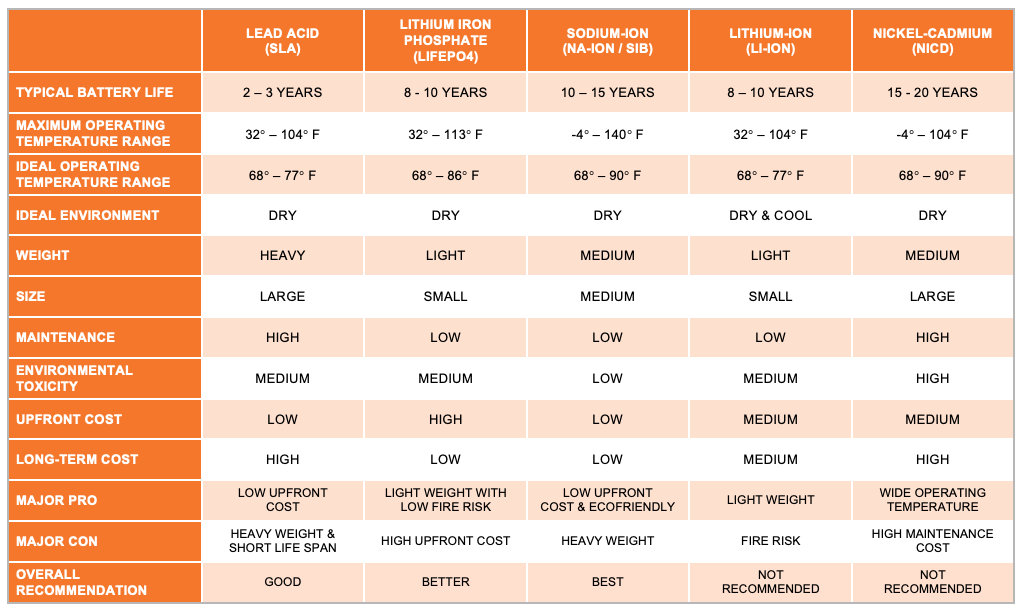
Lead Acid (SLA)
Lead acid batteries are one of the most commonly used constructions in UPSs. They are reliable, cost-effective, easy to manufacture and offer a relatively large storage capacity; however, they have a shorter lifespan, heavier weight and occupy a much larger footprint than other battery types. Lead acid UPSs are generally cheaper to purchase upfront, but their short life makes them a much costlier option overtime — especially when used in larger whole-building and mission-critical systems.
Another drawback with lead acid batteries is their environmental impact. Lead is a toxic material that requires specialized handling and disposal, and lead acid batteries tend to recharge inefficiently causing them to draw more power than other UPS options.
- Typical Battery Life: 2 – 3 years
- Upfront Cost: Low
- Long-Term Cost: High
- Maintenance: High
- Maximum Operating Temperature: 32 – 104 degrees F
- Environmental Impact: Medium
 Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4)
Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4)
Lithium iron phosphate batteries are rapidly gaining popularity with UPS manufacturers due to their long life, low maintenance and ecological benefits. Not to be confused with lithium-ion which we’ll discuss later, lithium iron phosphate technology is also safe and stable even in warm conditions. In fact, they tend to outperform most other battery formats — including lead acid — in high temperature environments.
Lithium iron phosphate batteries have a 3x greater average lifespan (8 – 10 years) than traditional lead acid technology with very little maintenance required. Additionally, they are non-toxic and don’t contain cobalt, a metal with environmental and ethical issues.
The downside to lithium iron phosphate is it’s upfront cost, and UPSs built with lithium iron phosphate batteries tend to have a higher initial cost but a lower overall cost considering their long life, low maintenance need and highly efficient performance.
- Typical Battery Life: 8 – 10 years
- Upfront Cost: High
- Long-Term Cost: Low
- Maintenance: Low
- Maximum Operating Temperature: 32 – 113 degrees F
- Environmental Impact: Medium
Sodium-Ion (Na-Ion / SIB)
Sodium-ion battery technology has seen a resurgence in recent years due to it’s low cost, wide temperature operating range, reliability and low ecological footprint. As their name implies, sodium-ion batteries use sodium ions to store and maintain an electric charge. Sodium, an abundant and low cost mineral, performs extremely well over long periods of time and in extreme conditions, and sodium-ion batteries are typically rated for 10 – 15 years in temperatures up to 140 degrees F.
The downside to sodium-ion technology is its low energy density, resulting in larger and heavier UPSs.
- Typical Battery Life: 10 – 15 years
- Upfront Cost: Low
- Long-Term Cost: Low
- Maintenance: Low
- Maximum Operating Temperature: -4 – 140 degrees F
- Environmental Impact: Low
Lithium-Ion (Li-Ion)
Not to be confused with lithium iron phosphate which we discussed above, lithium-ion technology is being phased out of UPS use due to thermal concerns. As noted with consumer electronics, lithium-ion batteries can overheat uncontrollably, releasing gas and potentially causing a fire or explosion when damaged or operated in a hot environment.
That said, lithium-ion technology is still used due to its moderate cost and longer lifespan; however, regular inspection is recommended.
- Typical Battery Life: 8 – 10 years
- Upfront Cost: Medium
- Long-Term Cost: Medium
- Maintenance: Low
- Maximum Operating Temperature: 32 – 104 degrees F
- Environmental Impact: Medium
Nickel-Cadmium (NiCd)
Nickel-cadmium batteries have largely been phased out of UPS use due to their high overall cost and negative environmental impact. Though they have a long lifespan (15 – 20 years), nickel-cadmium batteries tend cost more than other battery constructions due to required maintenance and difficulties with manufacturing.
Additionally, nickel-cadmium batteries contain both nickel and cadmium — two highly toxic materials — making disposal difficult. Combine this with a large physical footprint and a tendency to loose charge even when not being cycled, and nickel-cadmium has rapidly lost favor with most UPS manufacturers.
- Typical Battery Life: 15 – 20 years
- Upfront Cost: Medium
- Long-Term Cost: High
- Maintenance: High
- Maximum Operating Temperature: -4 – 104 degrees F
- Environmental Impact: High
Ready to purchase? Future Ready Solutions offers whole building and point-of-service UPS systems leveraging several of the technologies detailed above. Please contact us to discuss products and applications.